主要内容:
- 如何使用torchtext建立语料库
- 如何使用torchtext将词转下标,下标转词,词转词向量
- 如何建立相应的迭代器
torchtext预处理流程:
1. 定义Field:
声明如何处理数据
2. 定义Dataset:
得到数据集,此时数据集里每一个样本是一个 经过 Field声明的预处理 预处理后的 wordlist
3. 建立vocab:
在这一步建立词汇表,词向量(word embeddings)
4. 构造迭代器:
构造迭代器,用来分批次训练模型
实操
1. 下载数据:
kaggle:Movie Review Sentiment Analysis (Kernels Only)
train.tsv contains the phrases and their associated sentiment labels. We have additionally provided a SentenceId so that you can track which phrases belong to a single sentence.
test.tsv contains just phrases. You must assign a sentiment label to each phrase.
The sentiment labels are:
0 - negative
1 - somewhat negative
2 - neutral
3 - somewhat positive
4 - positive
下载得到:train.tsv和test.tsv
读取文件,查看文件
1 | import pandas as pd |
train.tsv
1 | data[:5] |

test.tsv
1 | test[:5] |

2. 划分验证集
1 | from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split |
3. 定义Field
首先导入需要的包和定义pytorch张量使用的DEVICE
1 | import spacy |
Torchtext采用了一种声明式的方法来加载数据:你来告诉Torchtext你希望的数据是什么样子的,剩下的由torchtext来处理。
实现这种声明的是Field,Field确定了一种你想要怎么去处理数据。
data.Field(…)
Field的参数如下:
sequential: Whether the datatype represents sequential data. If False, no tokenization is applied. Default: True.
use_vocab: Whether to use a Vocab object. If False, the data in this field should already be numerical. Default: True.
init_token: A token that will be prepended to every example using this field, or None for no initial token. Default: None.
eos_token: A token that will be appended to every example using this field, or None for no end-of-sentence token. Default: None.
fix_length: A fixed length that all examples using this field will be padded to, or None for flexible sequence lengths. Default: None.
dtype: The torch.dtype class that represents a batch of examples of this kind of data. Default: torch.long.
preprocessing: The Pipeline that will be applied to examples using this field after tokenizing but before numericalizing. Many Datasets replace this attribute with a custom preprocessor. Default: None.
postprocessing: A Pipeline that will be applied to examples using this field after numericalizing but before the numbers are turned into a Tensor. The pipeline function takes the batch as a list, and the field’s Vocab. Default: None.
lower: Whether to lowercase the text in this field. Default: False.
tokenize: The function used to tokenize strings using this field into sequential examples. If “spacy”, the SpaCy tokenizer is used. If a non-serializable function is passed as an argument, the field will not be able to be serialized. Default: string.split.
tokenizer_language: The language of the tokenizer to be constructed. Various languages currently supported only in SpaCy.
include_lengths: Whether to return a tuple of a padded minibatch and a list containing the lengths of each examples, or just a padded minibatch. Default: False.
batch_first: Whether to produce tensors with the batch dimension first. Default: False.
pad_token: The string token used as padding. Default: “
unk_token: The string token used to represent OOV words. Default: “
pad_first: Do the padding of the sequence at the beginning. Default: False.
truncate_first: Do the truncating of the sequence at the beginning. Default: False
stop_words: Tokens to discard during the preprocessing step. Default: None
is_target: Whether this field is a target variable. Affects iteration over batches. Default: False
例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16spacy_en = spacy.load('en')
def tokenizer(text): # create a tokenizer function
"""
定义分词操作
"""
return [tok.text for tok in spacy_en.tokenizer(text)]
"""
field在默认的情况下都期望一个输入是一组单词的序列,并且将单词映射成整数。
这个映射被称为vocab。如果一个field已经被数字化了并且不需要被序列化,
可以将参数设置为use_vocab=False以及sequential=False。
"""
LABEL = data.Field(sequential=False, use_vocab=False)
TEXT = data.Field(sequential=True, tokenize=tokenizer, lower=True)
4. 定义Dataset
The fields知道当给定原始数据的时候要做什么。现在,我们需要告诉fields它需要处理什么样的数据。这个功能利用Datasets来实现。
TabularDataset官网介绍: Defines a Dataset of columns stored in CSV, TSV, or JSON format.
对于csv/tsv类型的文件,TabularDataset很容易进行处理,故我们选它来生成Dataset
1 | """ |
注意:传入的(name, field)必须与列的顺序相同。
查看生成的dataset:
1 | print(train[5]) |
输出:
5. 建立vocab
我们可以看到第6行的输入,它是一个Example对象。Example对象绑定了一行中的所有属性,可以看到,句子已经被分词了,但是没有转化为数字。
这是因为我们还没有建立vocab,我们将在下一步建立vocab。
Torchtext可以将词转化为数字,但是它需要被告知需要被处理的全部范围的词。我们可以用下面这行代码:
1 | TEXT.build_vocab(train, vectors='glove.6B.100d')#, max_size=30000) |
这行代码使得 Torchtext遍历 训练集 中的绑定TEXT
field的数据,将单词注册到vocabulary,并自动构建embedding矩阵。
‘glove.6B.100d’ 为torchtext支持的词向量名字,第一次使用是会自动下载并保存在当前目录的 .vector_cache里面。
torchtext支持的词向量
- charngram.100d
- fasttext.en.300d
- fasttext.simple.300d
- glove.42B.300d
- glove.840B.300d
- glove.twitter.27B.25d
- glove.twitter.27B.50d
- glove.twitter.27B.100d
- glove.twitter.27B.200d
- glove.6B.50d
- glove.6B.100d
- glove.6B.200d
- glove.6B.300d
例:
如果打算使用fasttext.en.300d词向量,只需把上面的代码里的vector=’…’里面的词向量名字换一下即可,具体如下:
1 | TEXT.build_vocab(train, vectors='fasttext.en.300d') |
到这一步,我们已经可以把 词转为数字,数字转为词,词转为词向量 了
1 | print(TEXT.vocab.itos[1510]) |
输出: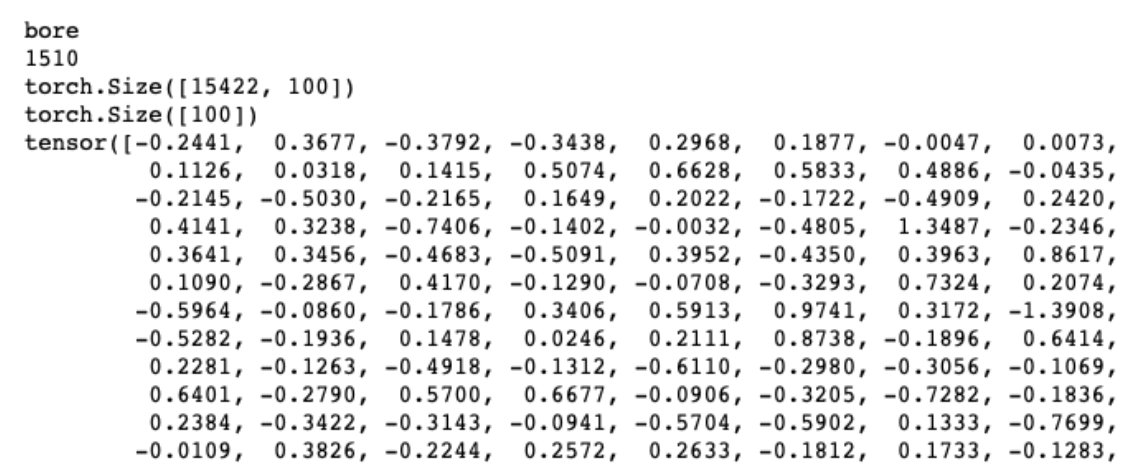
6. 构造迭代器
我们日常使用pytorch训练网络时,每次训练都是输入一个batch,那么,我们怎么把前面得到的dataset转为迭代器,然后遍历迭代器获取batch输入呢?下面将介绍torchtext时怎么实现这一功能的。
和Dataset一样,torchtext有大量内置的迭代器,我们这里选择的是BucketIterator,官网对它的介绍如下:
Defines an iterator that batches examples of similar lengths together.
Minimizes amount of padding needed while producing freshly shuffled batches for each new epoch.
1 | train_iter = data.BucketIterator(train, batch_size=128, sort_key=lambda x: len(x.Phrase), shuffle=True,device=DEVICE) |
迭代器使用
方法一1
2
3
4
5batch = next(iter(train_iter))
data = batch.Phrase
label = batch.Sentiment
print(batch.Phrase.shape)
print(batch.Phrase)
输出结果:
可以发现,它输出的是word index,后面的128是batch size
方法二1
2
3for batch in train_iter:
data = batch.Phrase
label = batch.Sentiment
7. 完整代码
1 | import spacy |